What to look for?
001
How did I leverage AI throughout the process to build an AI product for a edu tech startup?
Project Info
002
Timeline
6 months
Role
Lead Product Designer
Team
Zhiyuan Chen (Lead Designer)
Tina Chen (Designer)
Shivang Gupta (Head of Product)
Bill Guo (Design Manager)
Zach Levonian (Developer)
Methods
Focus Group
Ideate w/ AI & Prompt Engineering
Data Analysis
Rapid Prototyping
Participatory Design
Overview
003
What is PLUS?
Led by Carnegie Mellon University and Stanford University, PLUS is a tutoring platform that combines human and AI tutoring to bridge opportunity gaps in math education.
3000 +
middle school students
500 +
math tutors
3000 +
tutoring hours per week
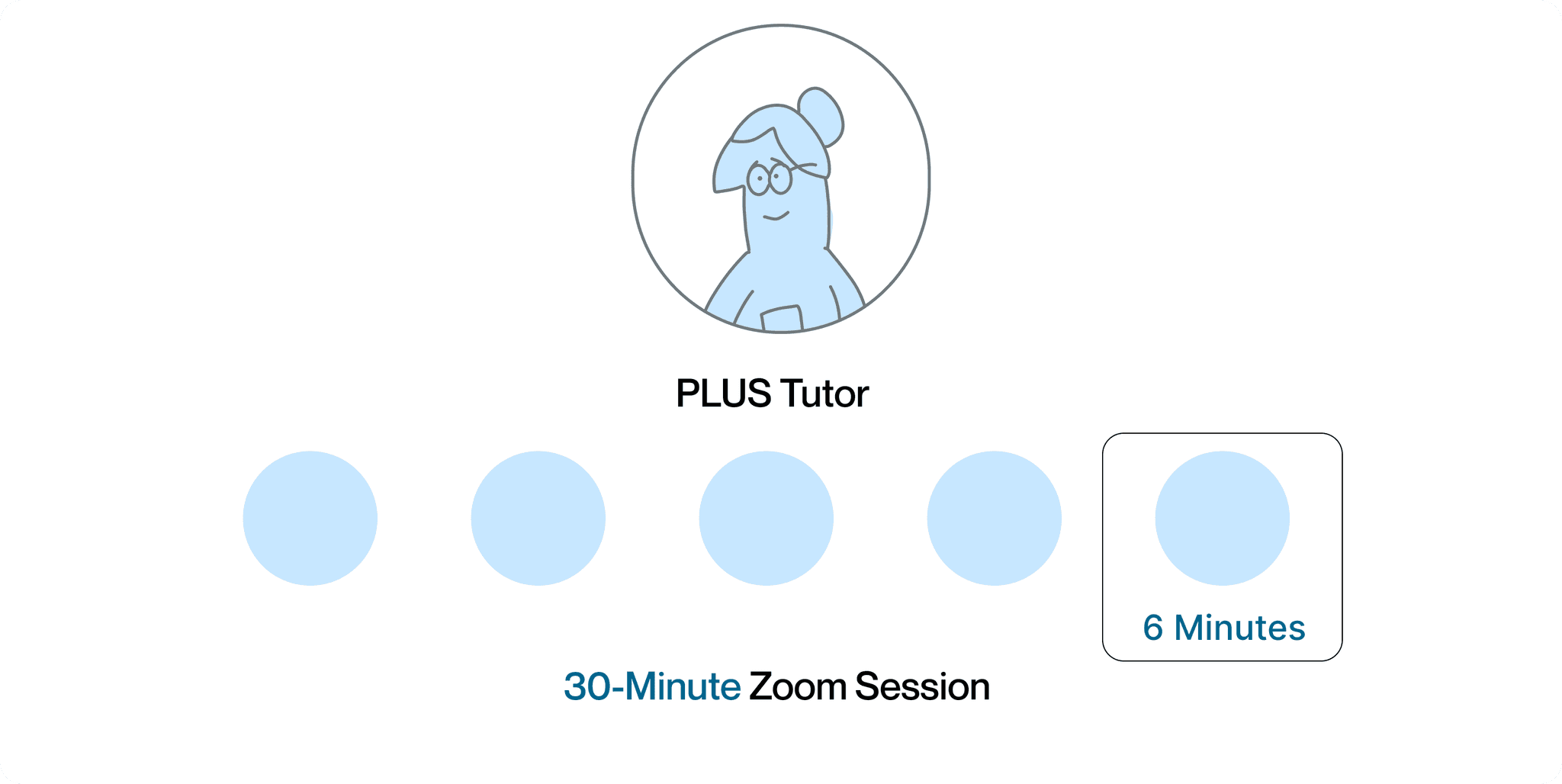
Problem: Tutors found themselves racing against the clock
Tutors at PLUS conduct 30-minute sessions with about 5 students, giving them only 6 minutes per student on average. This limited time makes it difficult for tutors to effectively address math problems, often resulting in subpar explanations or exceeding the allotted time, which negatively impacts other students' learning experiences.
Requirement: Embracing the trend of AI
Following the wave of Al, the Head of Product wants us to design an LLM-powered solution to help tutors with this issue.
Solution: Empowering tutors with a co-pilot
We developed an LLM-powered co-pilot to assist tutors clearly explain math problems, provide effective encouragement, and ask strategic leading questions, thereby reducing their cognitive load and supporting their goal of creating effective and engaging tutoring sessions.
Impact: Improving session efficiency
300 +
MAU
20%
decrease in time spent explaining math concepts
38%
increase in student engagement
End Results
004
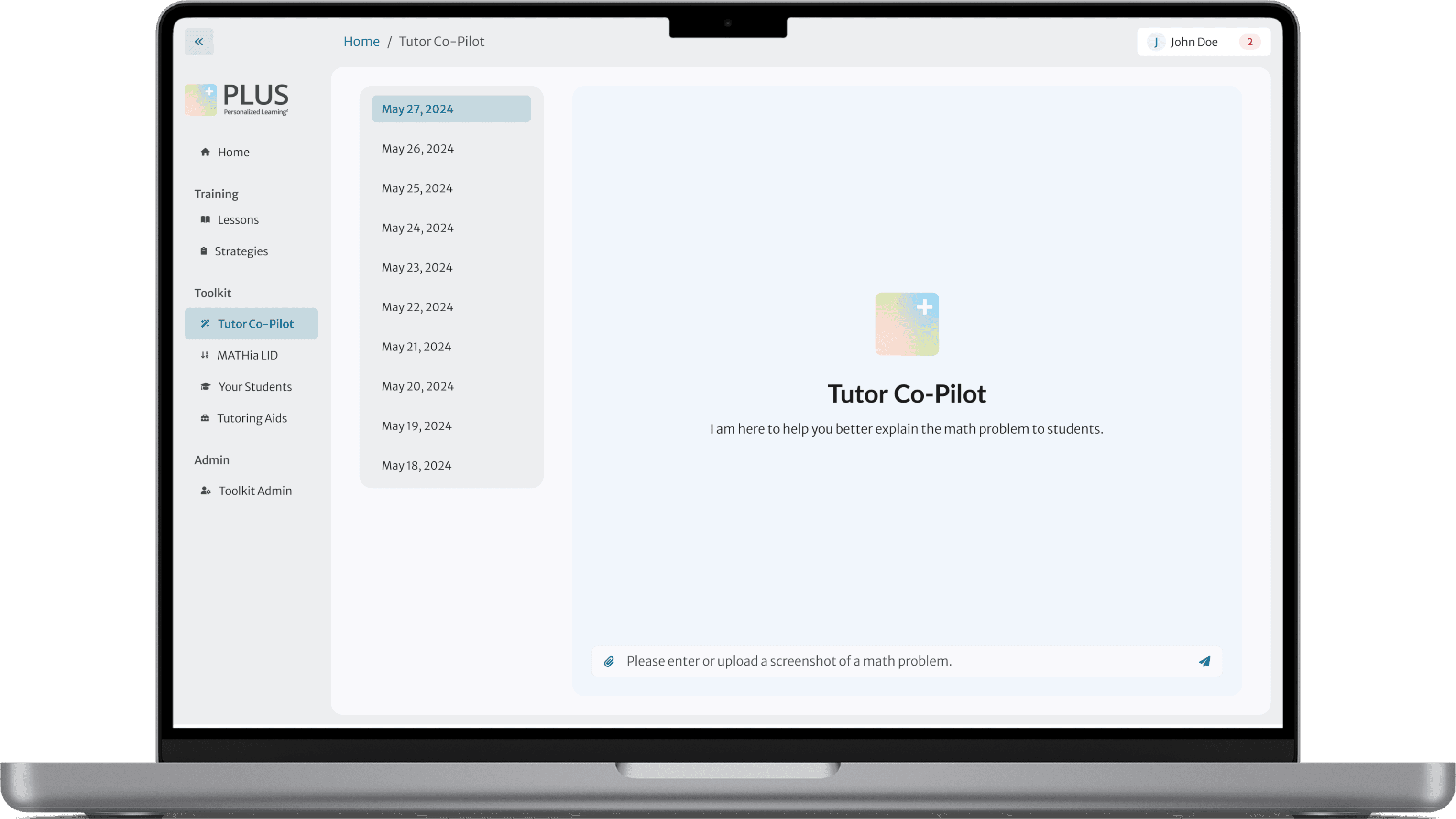
Enter or upload a math problem and Co-pilot generates a step-by-step guide, encouraging phrases, and leading questions to assist tutors with explaining problems and engaging students.
Ask followup questions or ask to extend or reduce the number of steps.
Provide quick and impactful feedback for developers in no time!
Research
005
Identifying user pain points
12 Video Analysis
Understand session structure
Observe tutor and student behaviors and interaction patterns
Identify challenges and frictions
2 Focus Group Interviews
Understand tutors' pain points, including when they occur, their frequency, and severity
Understand how they manage challenges and the support available to tutors
Mapping user pain points and the level of existing support onto various phases
Defining project scope
Focus on In-Session Phase
The numerous pain points and inadequate existing support highlight a significant opportunity for intervention during the session, where help is most needed.
Focus on Controllable Pain Points
Some pain points are not manageable through design intervention and are therefore out of scope. Consequently, we discarded those and focused only on the ones we can address
Ideation
006
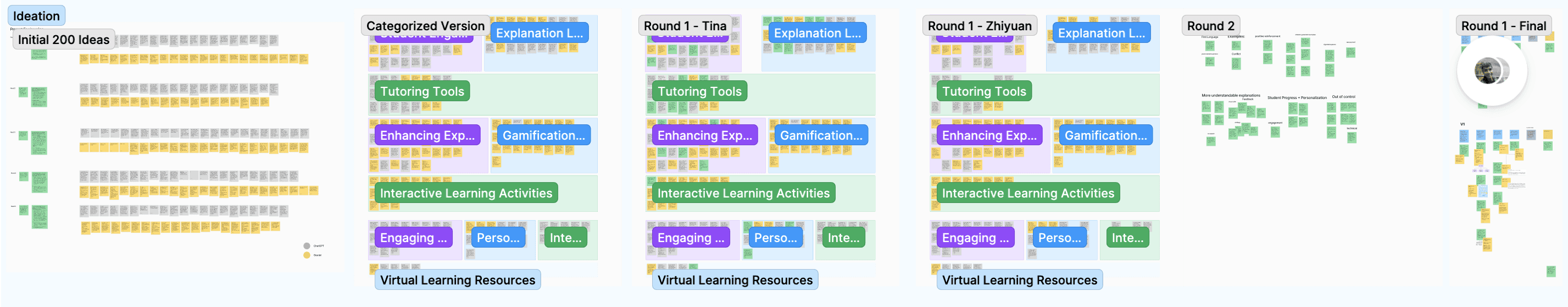
From 0 to 200:
A wild diverge with AI-driven brainstorming
We generated 200 ideas using Gen-AI to overcome design fixation from conventional methods like Crazy 8s and Creative Matrix.
We went through 3 iterations in prompt engineering where we simultaneously evaluate input and output to find the most effective prompt that lead to most reliable ideas.
The ideas before were out of scope and impractical whereas the ideas after are applicable and innovative.
Convergence
007
From 200 to 2: Synthesizing Internal & External Feedback
After several rounds of initial filtering, we trimmed our potential ideas from 200 to 10. We then used multi-method approaches to seek input from different stakeholders to further narrow down ideas and eventually landed on 2 solutions that are high-impact and low-effort
➡️ Solution I
A step-by-step guide to math problems for tutors to provide explanations effeciently
➡️ Solution II
Strategic leading questions for tutors to ask students instead of offering answers directly
Rapid Prototyping
008
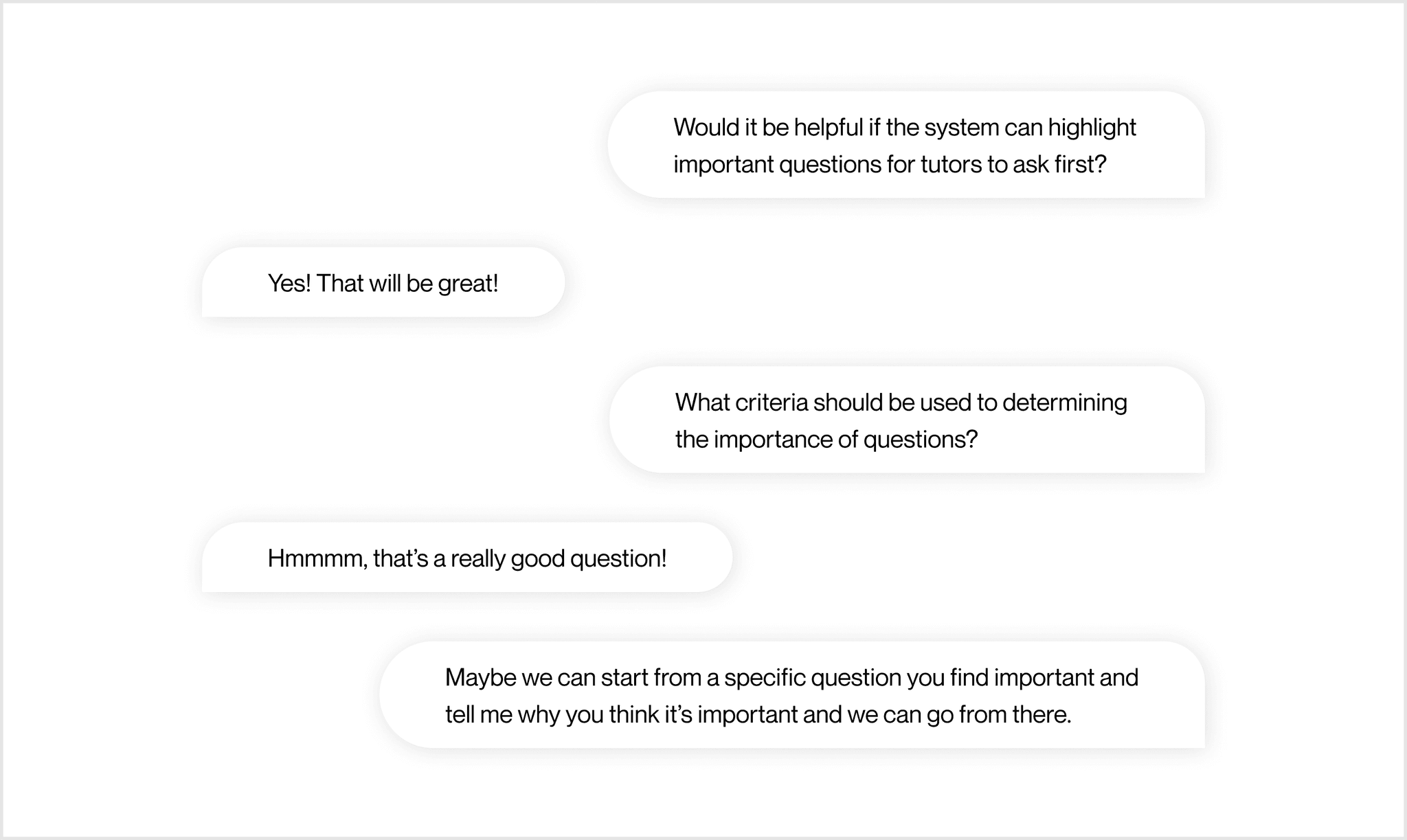
Co-create the solution by training GPT models with 5 tutors for useful and desirable model output
Although the design direction is clear, we don't know what output would be helpful at the content level. To develop a language model that's useful and desirable for users, we conducted 5 participatory design sessions, inviting tutors to train a model together.
Final Design
009
Model Iterations
010
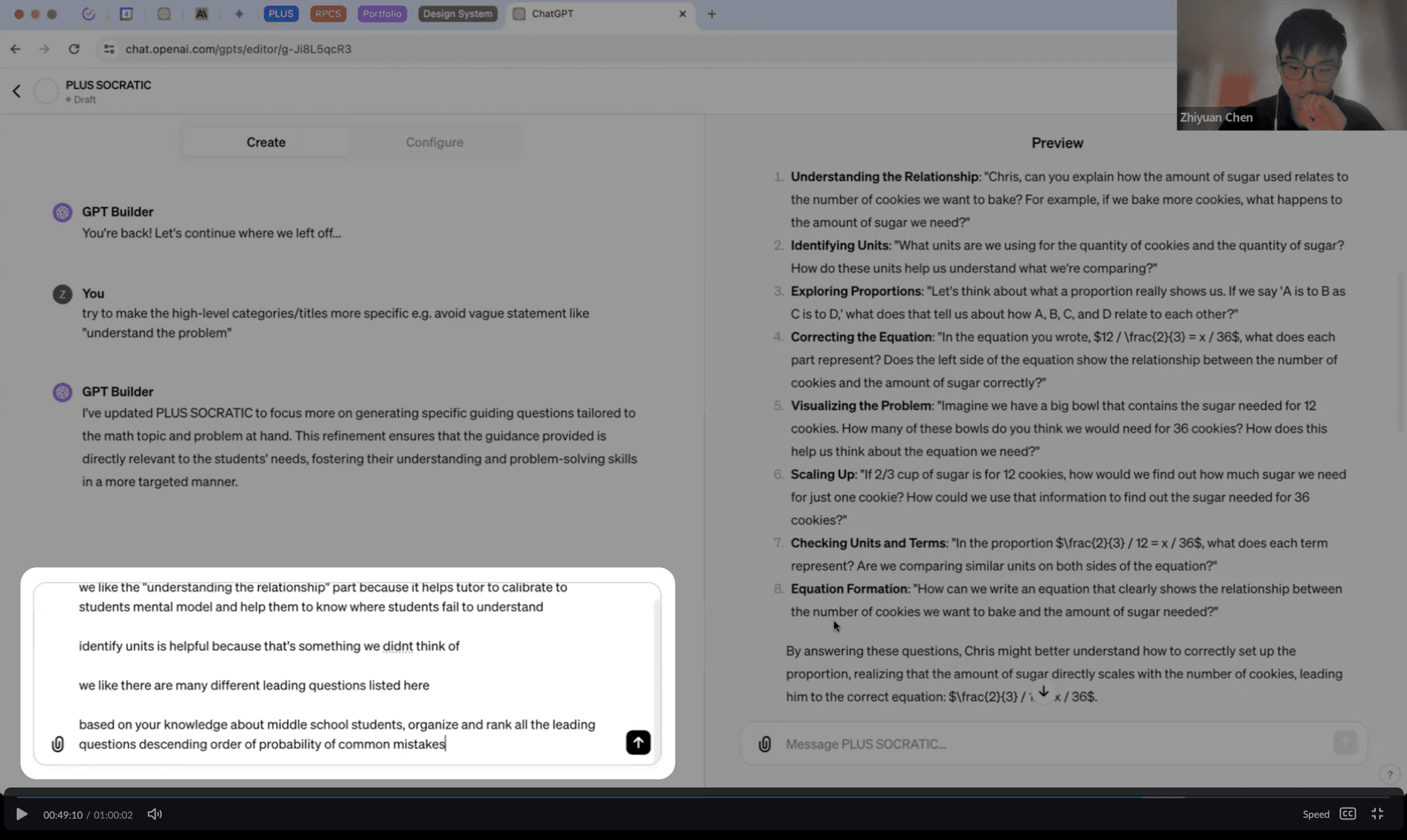
Synthesize feedback from SMEs on the model and translate into actionable steps for Devs
To continuously enhance model output, I conducted two rounds of feedback collection from tutor supervisors. I synthesized this feedback into concrete and actionable steps for developers to iterate on.
Initial feedback, unstructured and wordy
Synthesized feedback, contextual, actionable and with examples
Reflection
011
Incorporating AI into the process
Designing AI solutions has unveiled a whole new array of techniques and skills distinct from traditional product design. For example, the GPT co-design process emphasizes rapid prototyping, leveraging real-time feedback to significantly enhance efficiency. Initially, this novel approach felt overwhelming, but delving into these new methods has been immensely gratifying. This experience has honed my adaptability and enriched my skill set, making me a more versatile and resilient designer.
Over-communication for success
Given the innovative design process, I emphasized clear communication with stakeholders. I provided regular progress updates, outlined their contributions at each stage, and explained design decisions in detail. This transparency built trust and kept the project moving smoothly despite uncertainties, fostering collaboration and cohesion throughout development.